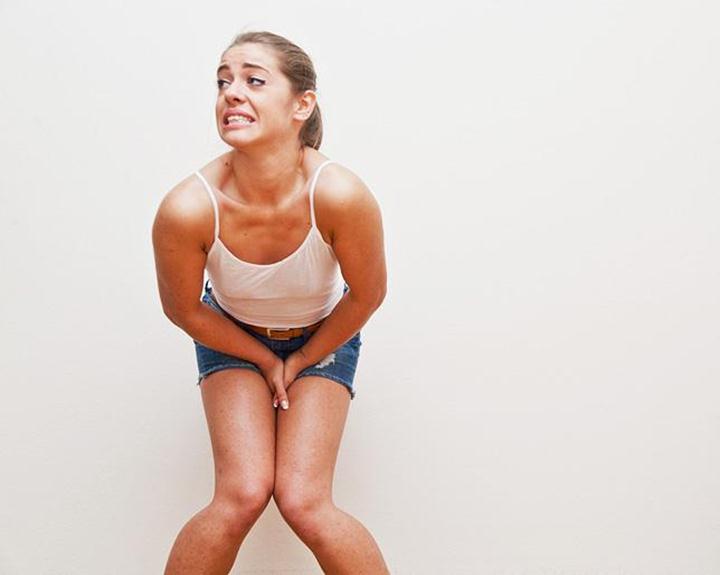
“What exactly is a UTI?” is such a common question. The term UTI or ‘urinary tract infection’ is a general term commonly used to define body disorders that are characterized by the blood in one’s urine, difficulty urinating, frequent urination or even urinating accidentally. Other interchangeable terms include Feline Idiopathic Cystitis or the (FIC), Feline Urologic Syndrome or Interstitial Cystitis. All these are treatable conditions that see an infection in one’s bladder and/ or the urethra of the lower urinary tract — in other words the tube that takes waste from your bladder to be urinated out of your body.
Symptoms and Types
Both men and women can suffer from these types of infections. The symptoms that may indicate one of these conditions include:
- Difficult or painful urination (stinging/ burning)
- Urine that has blood in it
- Urinating more frequently than usual or in abnormal amounts
- Blockage of the flow of urine
- An extremely strong urge to urinate and then an inability to do so
- Pains in the lower back
In addition, an examination by a medic may also show that the person is suffering from a firm, thickened, contracted bladder wall, which is generally only discovered during a physical examination.
These symptoms can also point to other conditions or conditions that can lead to more serious diseases, so a more thorough examination may be needed to ascertain exactly which condition the person is suffering from.
Causes and Diagnosis
The reasons for these conditions isn’t entirely known, but there are a number of potential causes. One includes a non-infectious disease such as interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome. Other viruses such as calicivirus or gamma herpesvirus can also cause the conditions. Often some of these circumstances will lead to bacteria or the white blood cells in your urine while stress can bring on the condition or make an existing condition worth.
As mentioned, an expert will need to conduct a thorough examination to decide which condition is affecting the patient and what treatment is needed. Sometimes the cause is a metabolic disorder such as kidney stones or an obstruction in the system. Other times it may be due to a parasite, a bacterial or a fungal infection. A physical exam will help with some of these matters while an x-ray may be needed to locate stones. A cystoscopy may be needed to see if there are any stones, cysts and polyps causing a blockage.
Treatment
If there is no blockage present, then the professional will typically deal with the condition, only referring the patient to a hospital if a procedure is needed to remove something. Medical observation might be essential if there are crystals in one’s urine while eating moist food instead of dry food to manage this. Prescriptions may be needed if there is an infection of a kind that requires treatment. And these usually prescribe a dose of antibiotics to kill the infection.
Sourced from: DUGOUT
Photo: womenshealthmag